Top 7 Key Types of Artificial Intelligence
The digital age has ushered in an unprecedented technological advancement era, and at its forefront stands types of artificial intelligence. If you notice the world around us, from pop-up ads on streaming services to self-driving cars, AI has permeated nearly every facet of our modern lives. But the term “artificial intelligence” often conjures up a monolithic image, a singular entity capable of performing complex tasks.
In reality, AI is far more nuanced, comprising a spectrum of distinct categories based on its capabilities and functionalities. Understanding these different types is crucial to grasping the true potential and limitations of this transformative technology. So, let’s embark on a journey to decode the fascinating world of AI and explore its seven key classifications.
The Ever-Evolving World of AI

Imagine a world where machines can not only perform tasks efficiently but also learn from their experiences. They are able to understand human intentions and even exhibit a form of consciousness. While the latter might still reside in science fiction, the rapid progress in developing types of artificial intelligence is steadily pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Indeed, Gartner’s study predicts that by 2028, 33% of enterprise software applications are expected to feature agentic AI. It’s a sharp increase, considering the percentage was under 1% in 2024. This staggering statistic underscores the pervasive influence of AI and the urgent need for an understanding of its various forms.
At its core, AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think and act like humans. However, this broad definition encompasses a diverse range of AI systems, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Next up, we will delve into the intricacies of these different artificial intelligence types.
7 Key Types of Artificial Intelligence
The realm of artificial intelligence can be broadly categorized based on its capabilities and level of sophistication. These categories range from simple, reactive systems to the hypothetical pinnacle of self-aware machines. Here’s a summary of the 7 AI types:
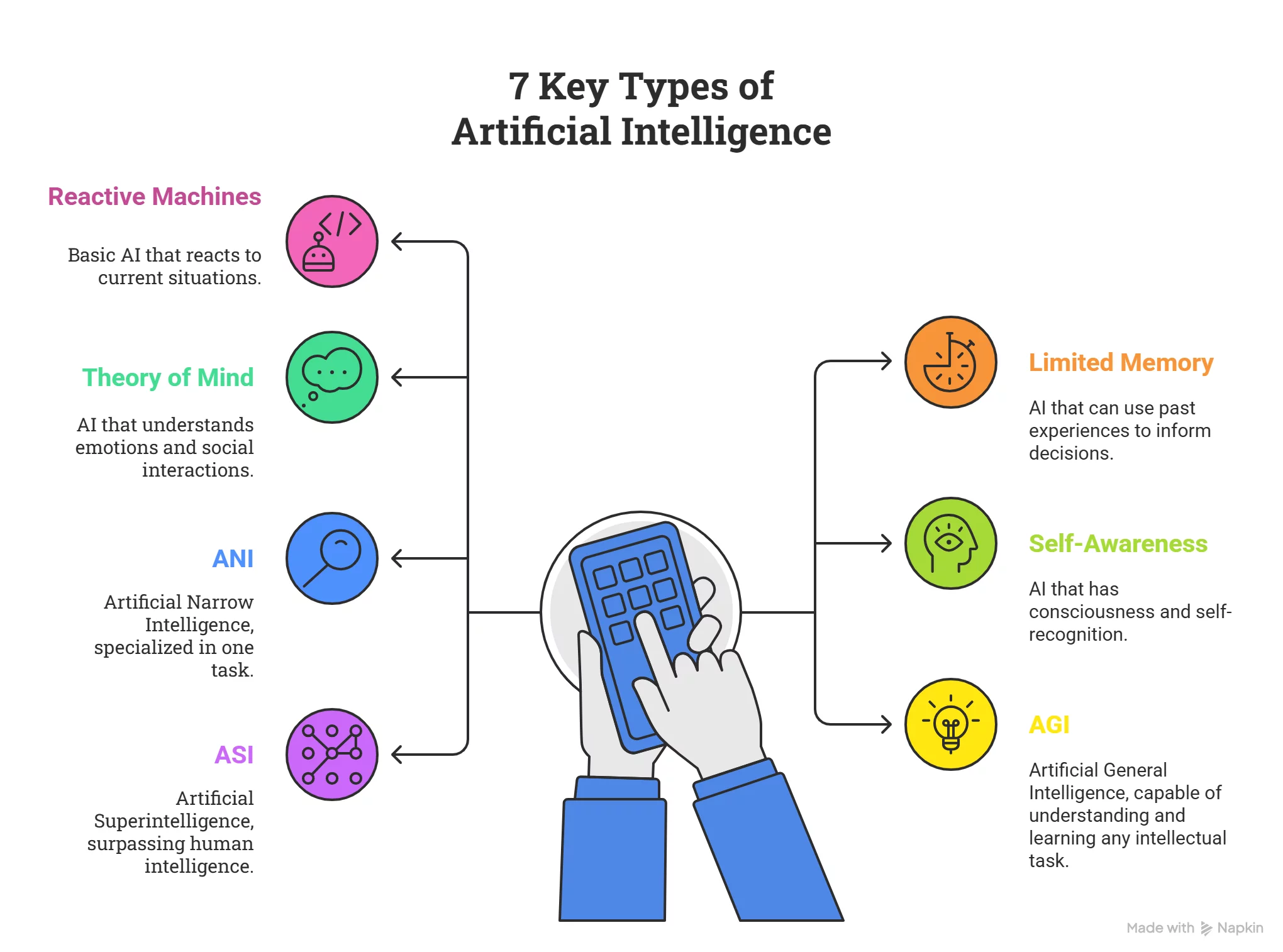
Let’s explore these seven distinct types of artificial intelligence in detail:
Reactive Machines
At the foundational level of AI lies the category of reactive machines. These are the most basic types of AI systems. Typically, they’re characterized by their ability to only react to the present situation based on pre-programmed rules. Consequently, they possess no memory of past experiences, nor can they learn or adapt over time.
A classic example is Deep Blue, the IBM supercomputer that famously defeated chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov in 1997. Deep Blue could analyze the current board state and make optimal moves based on its vast database of chess strategies. Similarly, many simple recommendation systems that suggest products based on your current Browse activity fall into this category. While limited in their scope, reactive machines excel in specific, well-defined tasks where historical data or learning is not required.
Limited Memory
Moving up the complexity ladder, we encounter the types of artificial intelligence systems with limited memory. Unlike reactive machines, these systems can store past information for a short period, allowing them to make more informed decisions. This ability to retain recent data is crucial for tasks that require understanding sequences or patterns.
Consider self-driving cars, for instance. They need to remember the speed and position of nearby vehicles, the trajectory of pedestrians, and recent traffic signals to navigate safely. Correspondingly, voice chatbots, designed to recall earlier parts of a conversation to deliver contextually relevant responses, also rely on limited memory. Thus, this type of AI represents a significant step forward from reactive machines, enabling more sophisticated and context-aware applications.
Theory of Mind
Venturing into more advanced and currently largely theoretical territory, we find the concept of “Theory of Mind” AI. This type of AI would understand that other entities, whether humans, machines, or other AI, have beliefs, desires, and intentions. Moreover, these types of artificial intelligence systems would recognize that emotions can also influence their behavior. In essence, it would have a form of social intelligence capable of understanding and predicting the mental states of others.
While current AI systems can mimic some aspects of human interaction, they lack a genuine understanding of emotions and intentions. The development of true Theory of Mind AI would revolutionize human-computer interaction. Ultimately, it leads to more empathetic and collaborative robots and virtual assistants. However, this remains a significant research challenge, requiring breakthroughs in areas like natural language understanding, emotional recognition, and common-sense reasoning.
Self-Awareness
The pinnacle of AI, at least from a theoretical standpoint, is self-awareness. This hypothetical AI type would not only understand its existence but also possess consciousness, feelings, and a sense of self. Owing to this, it would be aware of its own internal states and be able to reason about them.
Whilst often depicted in science fiction, self-aware types of artificial intelligence are currently purely speculative and far beyond our current technological capabilities. Achieving true self-awareness in machines raises profound philosophical and ethical questions about consciousness, sentience, and the very definition of life. Although the prospect is fascinating, it’s important to emphasize that we’re nowhere near creating AI with this level of sophistication.
Weak AI – Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
In stark contrast to the theoretical realms, ANI is the most prevalent type of AI in use today. ANI is designed and trained to perform a specific task or a narrow set of tasks. Particularly, it excels within its defined domain but lacks the general intelligence and adaptability of humans.
Examples of ANI are ubiquitous in our daily lives. Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are prime examples of these types of artificial intelligence. They’re capable of understanding and responding to voice commands within specific parameters. Image recognition software that can identify objects in photos and spam filters that weed out unwanted emails. Even sophisticated medical diagnosis systems that focus on a particular disease all fall under the umbrella of ANI.
As you can see, ANI is limited in scope, but it has proven incredibly valuable. It helps automate tasks, improve efficiency, and deliver specialized solutions across various industries.
Strong AI – Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Bridging the gap between the specialized capabilities of ANI and the hypothetical consciousness of self-aware AI is AGI. AGI represents AI with the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, much like a human being. It would possess human-level cognitive abilities, capable of reasoning, problem-solving, learning, and understanding complex concepts across diverse domains.
Unlike ANI, which excels in a specific niche, AGI would be adaptable and capable of tackling unfamiliar problems. It is one of the most advanced types of artificial intelligence and a major focus of ongoing research. The potential impact of AGI is immense, promising breakthroughs in fields ranging from scientific discovery to creative arts. However, the path to achieving true AGI is fraught with technical and conceptual challenges.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
Finally, we arrive at the hypothetical realm of Artificial Superintelligence, as known as ASI. This represents a level of intelligence that surpasses human intelligence in virtually every field. In particular, it excels in areas such as creativity, problem-solving, general wisdom, and scientific innovation. An ASI would not only be smarter than the smartest human but also possess cognitive abilities far beyond human comprehension.
The emergence of ASI raises profound questions about the future of humanity. While it could potentially solve some of the world’s most pressing challenges, it also carries significant risks if not developed and managed responsibly.
In the meantime, these types of artificial intelligence remain firmly in the realm of science fiction. Nevertheless, its feasibility and potential implications are subjects of intense debate among researchers and ethicists.
Where Do These Types of AI Shine?
Whereas some artificial intelligence types remain theoretical, many are already deeply integrated into our lives. Let’s explore some real-world applications through the lens of case studies:
Reactive Machines in Finance
High-frequency trading (HFT) systems are a prime example of reactive machines, or shall we call finance AI, in action. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of market data in real-time and execute trades within milliseconds based on pre-programmed rules.
A case study by the World Federation of Exchanges highlighted how HFT has increased market liquidity and reduced trading costs. At the same time, it raised concerns about potential market volatility due to the rapid and automated nature of these trades. These types of artificial intelligence systems react purely to market fluctuations without any memory of past trends or an understanding of underlying economic factors.
Limited Memory in Customer Service
Chatbots powered by limited memory AI is revolutionizing customer service. For instance, consider the case study of KLM Royal Dutch Airlines. Their chatbot, “Blue,” can handle over 1.7 million conversations per year. It’s been answering customer queries about flight bookings, baggage allowances, and more.
Blue remembers the context of the conversation, allowing it to provide more relevant and personalized assistance. This limited memory capability significantly improves customer satisfaction and reduces the workload on human agents for routine inquiries.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence in Healthcare
The healthcare industry has witnessed significant advancements through the application of ANI. A compelling case study is that of Google’s DeepMind, now called Google Health. The company has developed an AI system to detect eye diseases like diabetic retinopathy.

These types of artificial intelligence systems were trained on thousands of retinal scans. Therefore, they’ve achieved diagnostic accuracy comparable to human ophthalmologists. This application of ANI has the potential to improve early detection and treatment of vision-threatening conditions significantly. Thus, it’s especially beneficial in areas with limited access to specialized medical professionals.
Others
We don’t yet have concrete case studies for other types of AI in widespread use. However, ongoing research in areas like social robotics aims to develop AI with rudimentary forms of understanding human intentions. Furthermore, the pursuit of AGI is driving innovation across multiple fields. Its potential future applications include scientific research, complex problem-solving, and creative endeavors.
The Journey Ahead: Ethical Considerations and Future Implications
As the capabilities of types of artificial intelligence continue to advance, it’s important to consider the ethical implications on society. The development and deployment of AI raise a multitude of questions that require careful consideration.
Bias and Fairness in Narrow AI
One significant ethical concern revolves around bias in AI algorithms, particularly within the realm of ANI. AI systems are trained on vast datasets. If these datasets reflect existing societal biases, the AI can perpetuate and even amplify these biases in its decision-making.
For example, facial recognition software has exhibited higher error rates for individuals with darker skin tones. It has highlighted the potential for discriminatory outcomes. Hence, addressing this requires careful curation of training data and ongoing efforts to ensure fairness and equity in AI systems.
Ethical Challenges of AGI and ASI
The prospect of AGI and ASI also raises profound ethical and societal questions. The potential impact on the job market is a major concern, as AI-powered automation could displace human workers in various industries.
As AI systems become increasingly intelligent and autonomous, it becomes essential to consider safety protocols and control mechanisms carefully. These measures are crucial to preventing unintended or harmful consequences. Moreover, the advancement of certain types of artificial intelligence raises deep philosophical questions. It prompts us to reflect on the nature of consciousness, the definition of intelligence, and humanity’s place in the universe.
The Exciting Future of AI
In conclusion, the world of types of artificial intelligence is a rich and multifaceted landscape. We’ve explored the seven key categories and their applications in the modern world throughout this blog. As AI continues its rapid evolution, understanding its various forms is essential. This knowledge helps us navigate the exciting and potentially revolutionary journey that lies ahead.
The ongoing research and development in the field promise a future where AI plays an even more integral role in our lives. It is up to us to ensure that this technology is harnessed responsibly and ethically for the betterment of humanity.