In today’s hyper-connected world, cybersecurity is a critical concern for businesses of all sizes. However, small businesses are particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks due to limited resources, lack of expertise, and the misconception that they are too small to be targeted. As we move into 2025, the cyber threat landscape is becoming more sophisticated, with attackers leveraging advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to exploit vulnerabilities.
For small businesses, the stakes are high. A single data breach can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and even business closure. According to recent studies, 60% of small businesses that suffer a cyberattack go out of business within six months. To avoid becoming a statistic, small businesses must adopt proactive and robust cybersecurity measures.
In this article, we’ll explore 10 cybersecurity best practices tailored for small businesses in 2025. These strategies will help you protect your business from evolving threats and ensure long-term resilience.
- 1) 1. Implement Strong Password Policies
- 2) 2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- 3) 3. Regularly Update Software and Systems
- 4) 4. Train Employees on Cybersecurity Awareness
- 5) 5. Secure Your Network with a Firewall and VPN
- 6) 6. Backup Data Regularly
- 7) 7. Use Endpoint Protection
- 8) 8. Adopt a Zero Trust Security Model
- 9) 9. Monitor and Respond to Threats
- 10) 10. Develop an Incident Response Plan
- 11) Conclusion
1. Implement Strong Password Policies
Why Passwords Matter
Passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Unfortunately, many employees still use weak or easily guessable passwords, such as “123456” or “password.” This makes it easy for cybercriminals to breach your systems.
Best Practices for Password Management
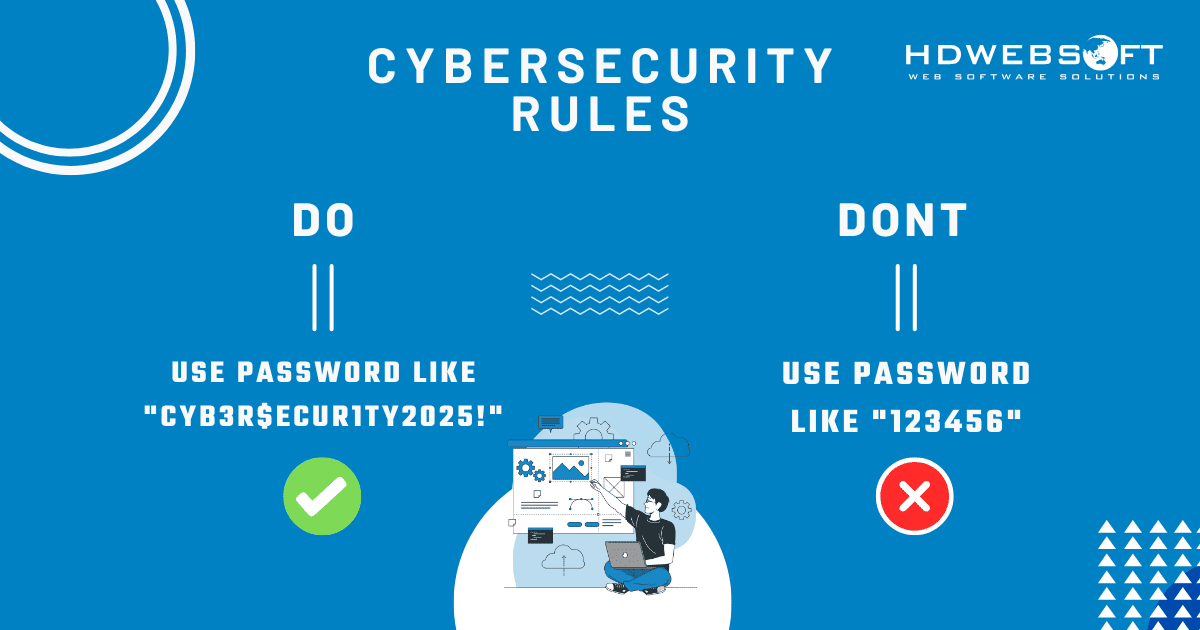
- Create Strong Passwords: Encourage employees to use passwords that are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid Reusing Passwords: Ensure that employees use unique passwords for each account to prevent a single breach from compromising multiple systems.
- Use a Password Manager: Password managers generate and store complex passwords securely, reducing the risk of human error.
- Enforce Regular Updates: Require employees to change their passwords every 60-90 days.
Example
Instead of using “admin123,” a strong password might look like this: “Cyb3r$ecur1ty2025!”.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
What is MFA?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before accessing an account. This could include something they know (a password), something they have (a smartphone), or something they are (a fingerprint).
Why MFA is Essential
Even if a hacker steals a password, they won’t be able to access the account without the second factor. According to Microsoft, MFA can block 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
How to Implement MFA
- Enable MFA for all critical systems, including email, cloud storage, and financial accounts.
- Use authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Authy instead of SMS-based codes, which can be intercepted.
3. Regularly Update Software and Systems
The Danger of Outdated Software
Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain access to systems. For example, the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 targeted computers running outdated versions of Windows.
Best Practices for Updates
- Enable Automatic Updates: Ensure that all software, operating systems, and firmware are set to update automatically.
- Patch Management: Regularly check for updates on devices that don’t support auto-updates, such as IoT devices.
- Retire Legacy Systems: Replace outdated hardware and software that is no longer supported by vendors.
Further reading: How do you Ensure Nodejs Security for Your Apps Development?
4. Train Employees on Cybersecurity Awareness
The Human Factor
Employees are often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Phishing attacks, for example, rely on tricking employees into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments.
How to Build a Security-Aware Culture
- Conduct Regular Training: Educate employees on recognizing phishing emails, social engineering tactics, and other common threats.
- Simulate Phishing Attacks: Test employees with mock phishing emails to identify areas for improvement.
- Create a Reporting System: Encourage employees to report suspicious activity immediately.
5. Secure Your Network with a Firewall and VPN
The Role of Firewalls
A firewall acts as a barrier between your internal network and external threats, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules.
The Importance of VPNs
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts internet traffic, ensuring secure communication between remote employees and your business network.
Implementation Tips
- Install a next-generation firewall (NGFW) that offers advanced features like intrusion prevention and deep packet inspection.
- Require employees to use a VPN when accessing company resources from public Wi-Fi or remote locations.
6. Backup Data Regularly
The Threat of Ransomware
Ransomware attacks encrypt your data and demand payment for its release. Without backups, you may lose critical information permanently.
Best Practices for Data Backup
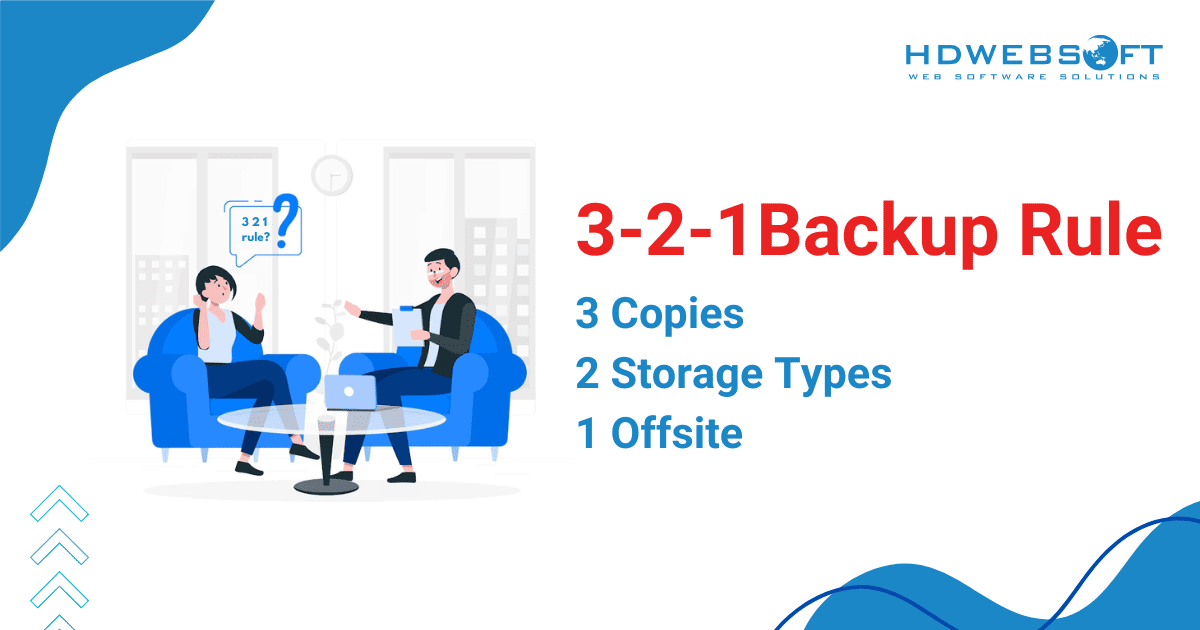
- Follow the 3-2-1 rule: Keep 3 copies of your data, on 2 different types of storage, with 1 copy stored offsite or in the cloud.
- Use automated backup solutions to ensure consistency.
- Test backups regularly to confirm they can be restored.
7. Use Endpoint Protection
What Are Endpoints?
Endpoints include devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets that connect to your network. These devices are common targets for cyberattacks.
How Endpoint Protection Works
Endpoint protection solutions detect and block malware, ransomware, and other threats in real-time. They also provide features like device encryption and application control.
Key Features to Look For
- Real-time threat detection.
- Automatic updates and patches.
- Centralized management for all devices.
8. Adopt a Zero Trust Security Model
What is Zero Trust?
The Zero Trust model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It assumes that no user or device, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default.
Steps to Implement Zero Trust
- Verify Identity: Use MFA and strong authentication methods.
- Limit Access: Grant users access only to the resources they need to perform their jobs.
- Segment Your Network: Divide your network into smaller segments to contain potential breaches.
9. Monitor and Respond to Threats
The Importance of Proactive Monitoring
Cyberattacks can go undetected for months, causing significant damage. Proactive monitoring helps you identify and respond to threats before they escalate.
Tools for Threat Monitoring
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collect and analyze security data from across your network.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Provide real-time visibility into endpoint activity.
10. Develop an Incident Response Plan
Why You Need a Plan
Even with the best defenses, a cyberattack may still occur. An incident response plan ensures that your team knows how to react quickly and effectively.
Read more: AI Testing: The Future of Quality Assurance
Key Components of an Incident Response Plan
- Preparation: Identify key roles and responsibilities.
- Detection and Analysis: Monitor for signs of a breach and assess its impact.
- Containment and Eradication: Isolate affected systems and remove the threat.
- Recovery: Restore normal operations and ensure systems are secure.
- Post-Incident Review: Analyze the incident to identify lessons learned and improve future responses.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve, small businesses must take a proactive approach to cybersecurity. By implementing these 10 best practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks in 2025. Remember, cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires vigilance, education, and adaptation.
Investing in cybersecurity today can save your business from costly breaches, reputational damage, and potential closure tomorrow. Stay informed, stay prepared, and prioritize your business’s digital safety.